Atmospheric Water Vapor Can Be Described as ________.
69 Vapor pressure can be described as A the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals atmospheric pressure B the pressure within the lungs during inhalation C the pressure exerted on the Earth by the particles in the sit. These variations are related to both weather and climate.
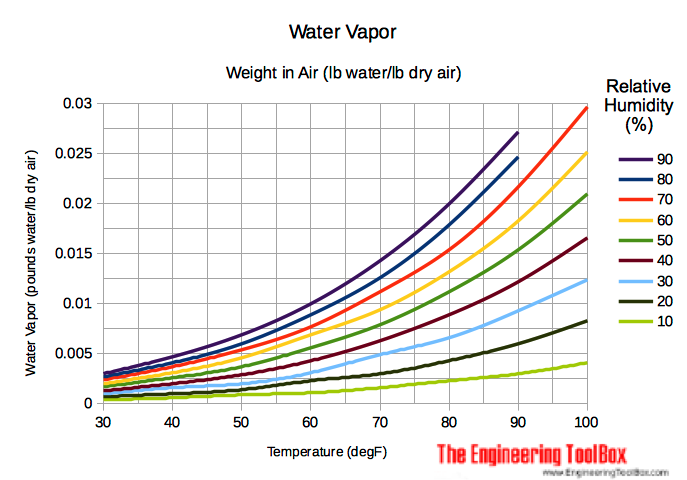
Moist Air Weight Of Water Vapor
404 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW Vol.

. The papers assess the state-of-the-art in measurement modeling and application of atmospheric water vapor properties and highlight important problems that require further effort in order to. ________ refers to water vapor leaving the Earths surface through plants. Atmospheric Water Vapor Adsorption.
The answer is because temperature sets a limit to how much water vapor can be in the air. Latent heat is an important source of energy especially for storms. The interactions of water vapor with other constituents of the atmosphere are complex and.
30 rows Atmospheric water vapor can be described as _____. There is a continuous exchange of water vapor between the atmosphere and dead wildland fuels. Atmospheric Water Vapor contains the technical proceedings of the International Workshop on Atmospheric Water Vapor held in Vail Colorado on September 11-13 1979.
Potential evapotranspiration is ________. Technical Abstract Limit 200 words The innovation addressed in this proposal is a. Water vapor in the atmosphere varies consid-erably in time and from place to place.
Through the use of molecular. We are concerned here with the small increase in trav el time caused by atmospheric water vapor. Water vapor is simply water in the gas phase ie individual molecules of H 2 O become part of the mixture of gases in the atmosphere.
Can be described by a continuous function nz where z is the height above the surface. Very small when the atmosphere is warm. Water vapor is extremely important in the atmosphere because.
Atmospheric moisture is a key element in fire weather. E fairly evenly distributed over time in most locations. Estimate the atmospheric column water vapor at reference wavelength λ of the scaled measured at-sensor radiance using the reference curve that was established in 4.
D the pressure exerted by a gas above the surface of its liquid. Early studies by Holtzman 15 and Benton Black-. B having an erratic distribution.
6 Water vapor can be described by all but one of the following. Vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by the vapors which are present on the surface of a liquid. A odorless b tasteless c a small fraction of the atmospheres volume d light blue color e energy-rich.
7 A considerable number of investigations of atmospheric water vapor flux and flux divergence as they relate to the hydrologic cycle of the earth-atmosphere system on scales ranging from less than lo5 km2 to hemispheric have been made during the past 15 years. Even in tropical air once the volume of water vapor in the atmosphere approaches 4 it will begin to condense out of the air. For Mars In Situ Resource Utilization.
Water vapor H2Ov is known to be a key agent in global scale processes including. For example vapor pressure of water at room temperature is 00313 atm. Atmospheric circulation weather radiative forcing and energy transfer.
Method for extracting water vapor from the. Releases large amounts of heat - called latent heat when it changes from vapor into water or ice. A composing most of the mass of the atmosphere in wet climates.
The condensing of water vapor prevents the percentage of water vapor in the air from increasing. 7 The saturated adiabatic lapse rate is a lesser lapse rate than the dry adiabatic lapse rate. Usually about the same as actual evapotranspiration.
Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air in a particular spot. Water vapor can best be described as a - gas. Chemistry questions and answers.
D most plentiful in the colder regions of Earth. If temperatures were much warmer. Use the estimate of atmospheric column water vapor to repeat from steps 1 to 5 until an acceptable level of convergence has been reached.
The one-way travel time t through the atmosphere is given by 1 j hsat t - nz dz C 0 1 where hsat is the geometric height of the satellite. It has direct effects on the flammability of forest fuels and by its relationship to other weather factors it has indirect effects on other aspects of fire behavior. It transforms into both liquid and solid cloud particles that grow and fall to Earth as precipitation.
Clouds are formed from water vapor. Usually not as great as actual evapotranspiration. If the humidity today is 80 percent it means that the air contains 80 percent of the total amount of water it can hold at that temperature.
Having an erratic distribution. Anthropogenic modification of atmospheric H 2Ov and the processes it influences are not as thoroughly studied on the urban or regional scale in comparison. Adding more energy or heat to liquid water raises its internal energy to the point the molecular bonds break and the substance becomes a gas known as water vapor.
On the other hand the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals atmospheric pressure is known as boiling point. C fairly evenly distributed by altitude. Water vapor is the primary greenhouse gas that helps control temperatures in the lower atmosphere.
Atmospheric water vapor can be described as ________. Water vapor can be described by all but one of the following. Which is NOT.
Atmosphere of Mars in an efficient lightweight and. We usually use the term to mean relative humidity the percentage of water vapor a certain volume of air is holding relative to the maximum amount it can contain. 5 Water that stays in liquid form at temperatures below freezing is ________.

What About Water Vapour Climate Change Connection

What About Water Vapour Climate Change Connection
Air Water Understanding Climate Ocean Surface Topography From Space
Comments
Post a Comment